What is Zonos TTS?
Zonos TTS AI is a text-to-speech (TTS) technology that enables the creation of highly expressive and natural-sounding speech from text inputs. It is designed to break language barriers by supporting multiple languages and offers advanced features like voice cloning, emotion control, and customization of speech parameters such as pitch and speaking rate.

Overview of Zonos TTS
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Model | Zonos-v0.1 |
| Description | Open-weight TTS model |
| Functionality | Generates natural speech from text. |
| Audio Quality | speech at 44kHz with control over rate, pitch, and emotions. |
| Multilingual Support | Supports English, Japanese, Chinese, French, and German. |
| Official Website | playground.zyphra.com/audio |
Zonos TTS: Usage
Step 1: Import Libraries
Action: Import the necessary libraries to use Zonos TTS.
What Happens: You will need to import PyTorch, torchaudio, and the Zonos model to get started.
import torch
import torchaudio
from zonos.model import Zonos
from zonos.conditioning import make_cond_dict
from zonos.utils import DEFAULT_DEVICE as deviceStep 2: Load the Model
Action: Load the pre-trained Zonos model.
What Happens: You can choose between different model versions. Here’s how to load the transformer model.
model = Zonos.from_pretrained("Zyphra/Zonos-v0.1-transformer", device=device)Step 3: Prepare Audio Input
Action: Load your audio file and create a speaker embedding.
What Happens: The audio file is loaded, and a speaker embedding is created for further processing.
wav, sampling_rate = torchaudio.load("assets/exampleaudio.mp3")
speaker = model.make_speaker_embedding(wav, sampling_rate)Step 4: Generate Speech
Action: Prepare the conditioning and generate the speech output.
What Happens: You create a conditioning dictionary and generate the speech based on the input text.
cond_dict = make_cond_dict(text="Hello, world!", speaker=speaker, language="en-us")
conditioning = model.prepare_conditioning(cond_dict)
codes = model.generate(conditioning)Step 5: Save the Output
Action: Decode the generated codes and save the audio file.
What Happens: The generated audio is saved as a WAV file for playback or further use.
wavs = model.autoencoder.decode(codes).cpu()
torchaudio.save("sample.wav", wavs[0], model.autoencoder.sampling_rate)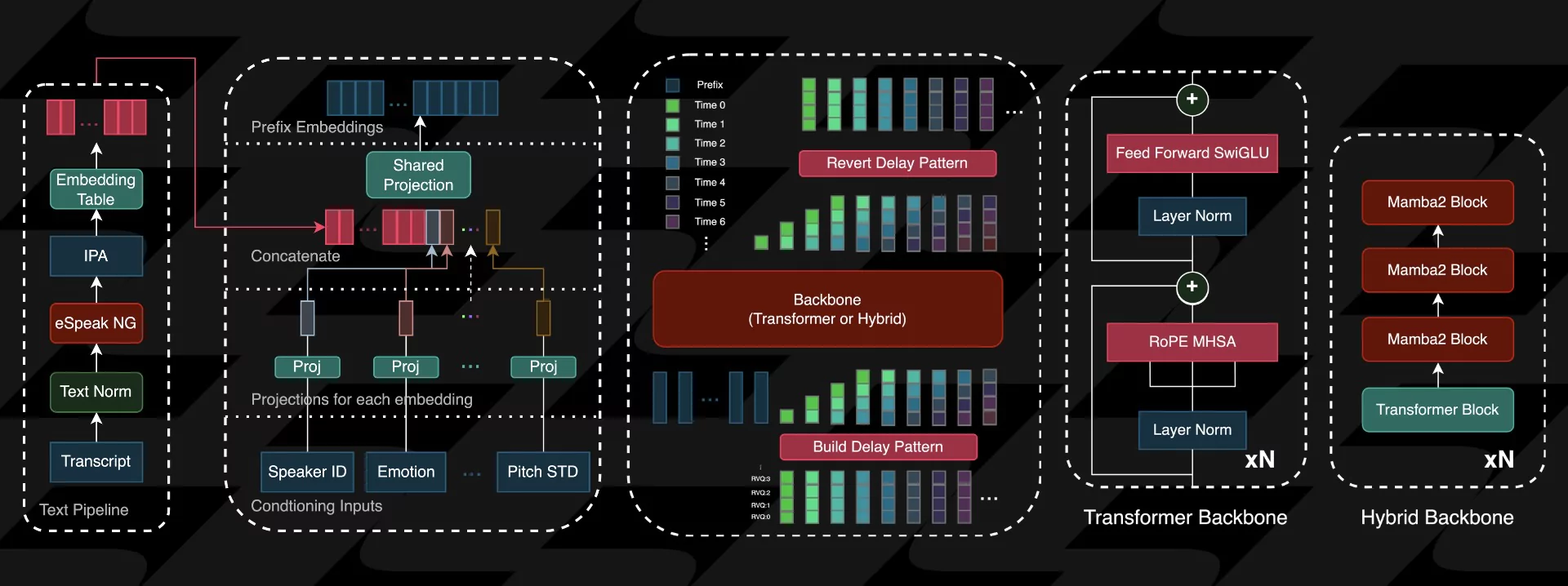
Gradio Interface (Recommended)
Action: Run the Gradio interface for an interactive experience.
What Happens: You can easily interact with the model through a web interface.
uv run gradio_interface.py
# python gradio_interface.pyKey Features of Zonos TTS
Zero-Shot TTS with Voice Cloning
Zonos allows users to generate speech by providing a short voice sample, typically between 3 to 30 seconds, enabling accurate voice replication.
Multilingual Support
It supports several major languages, including English, Chinese, Japanese, French, and German, making it versatile for global applications.
Emotion Control
Users can adjust the emotional tone of the speech, allowing for dynamic content creation with emotions like happiness, sadness, and surprise.
High-Quality Output
Zonos generates speech at a 44 kHz sample rate, ensuring high audio fidelity comparable to industry-leading solutions.
Open-Source Collaboration
The models are released under the Apache 2.0 license, encouraging community contributions and improvements.
Pros and Cons
Pros
- High-quality, expressive speech generation
- Supports voice cloning with minimal audio input
- Fine control over audio characteristics (pitch, rate, emotion)
- Multilingual support for diverse applications
- Fast processing with real-time performance on modern hardware
Cons
- Requires initial audio sample for voice cloning
- May be memory-intensive depending on usage
- Performance can vary based on input complexity
How to Use Zonos TTS AI?
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Ensure you have Python and the required libraries installed. Use the command:
pip install -U uvStep 2: Load the Model
Import the necessary libraries and load the Zonos model using:
model = Zonos.from_pretrained("Zyphra/Zonos-v0.1-transformer", device=device)Step 3: Prepare Audio Input
Load your audio file using:
wav, sampling_rate = torchaudio.load("assets/exampleaudio.mp3")Step 4: Create Speaker Embedding
Generate a speaker embedding with:
speaker = model.make_speaker_embedding(wav, sampling_rate)Step 5: Prepare Conditioning
Create a conditioning dictionary and prepare it:
cond_dict = make_cond_dict(text="Hello, world!", speaker=speaker, language="en-us")conditioning = model.prepare_conditioning(cond_dict)Step 6: Generate Audio
Generate the audio output:
codes = model.generate(conditioning)Step 7: Save the Output
Decode and save the generated audio:
wavs = model.autoencoder.decode(codes).cpu()torchaudio.save("sample.wav", wavs[0], model.autoencoder.sampling_rate)Step 8: Use Gradio Interface (Recommended)
For repeated sampling, run the Gradio interface:
uv run gradio_interface.py